The Greedycut algorithm iteratively removes from the dataset probes and samples of highest impurity. These correspond to the rows and columns in the detection p-value table that contain the largest fraction of unreliable measurements. This section summarizes the results of applying Greedycut on the analyzed dataset.
Unreliable Measurements
We considered every β value to be unreliable when its corresponding detection p-value is not below the threshold T:
p ≥ T = 0.05
The figure below summarizes the observed number of unreliable measurements per probe and per sample.
| Number of values per |
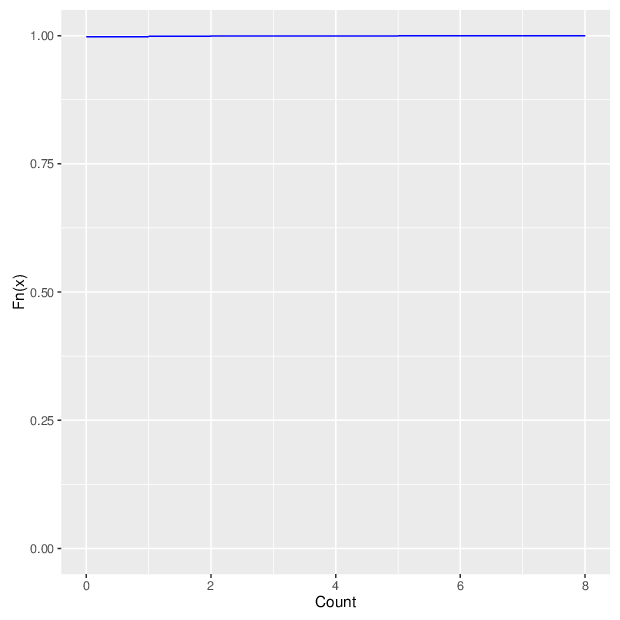
Cumulative distribution function of number of unreliable values per probe/sample.
Filtered Probes and Samples
RnBeads executed Greedycut using the threshold given above and applied all its steps. Briefly, Greedycut is an iterative algorithm that filters out the probe or sample with the highest fraction of unreliable measurements one at a time. Note that every iteration of the algorithm produces a matrix of retained measurements and a set of removed ones.
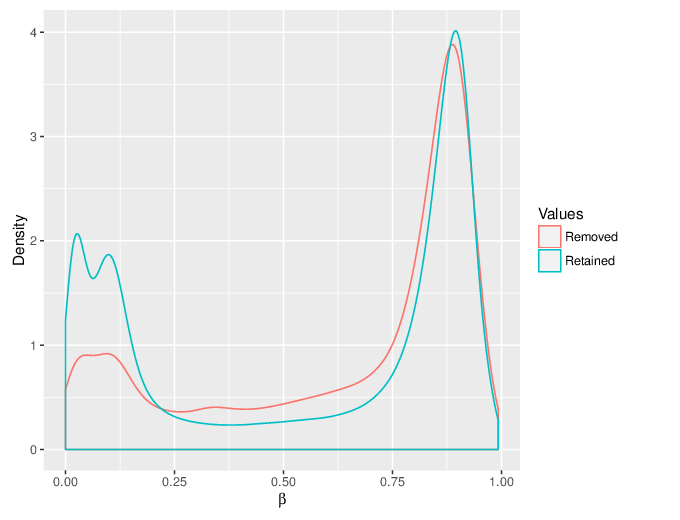
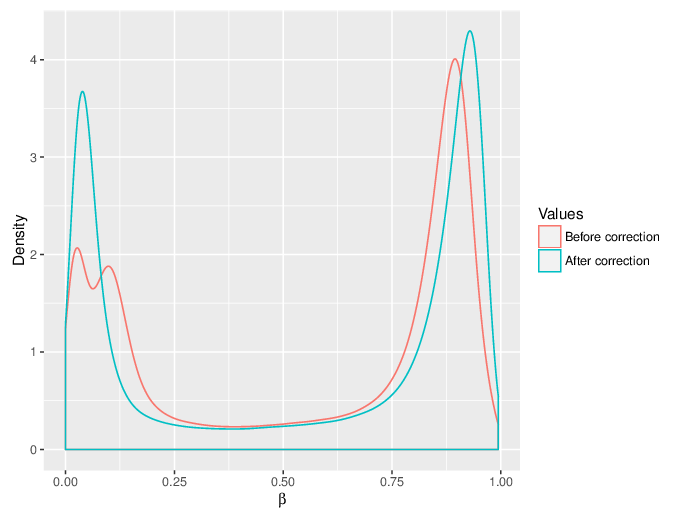
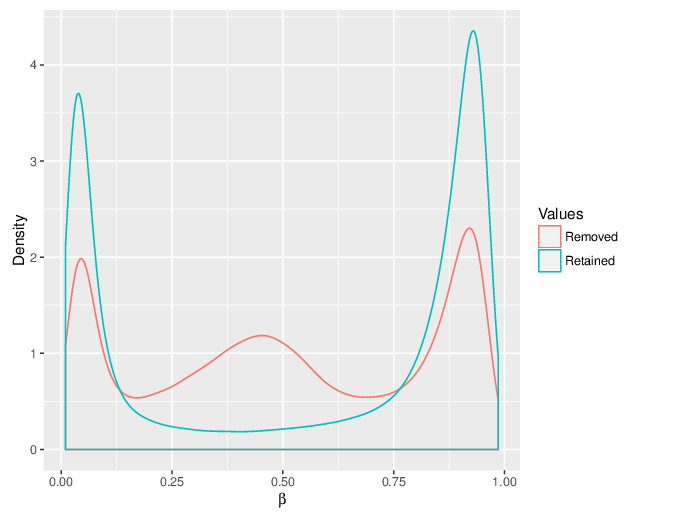
We calculated false positive rate (α) and sensitivity (s) when the retained measurements are considered as prediction for the reliable ones. Among all matrices produced by Greedycut, we selected the one that maximizes the value of the expression s + 1 - α, thereby giving equal weights to the sensitivity and specificity. Presented geometrically on a ROC curve, this is the point that is furthest from the diagonal. The results of the Greedycut procedure and the selected iteration are presented in the figure below.
| Metric | |
| Iterations to show |
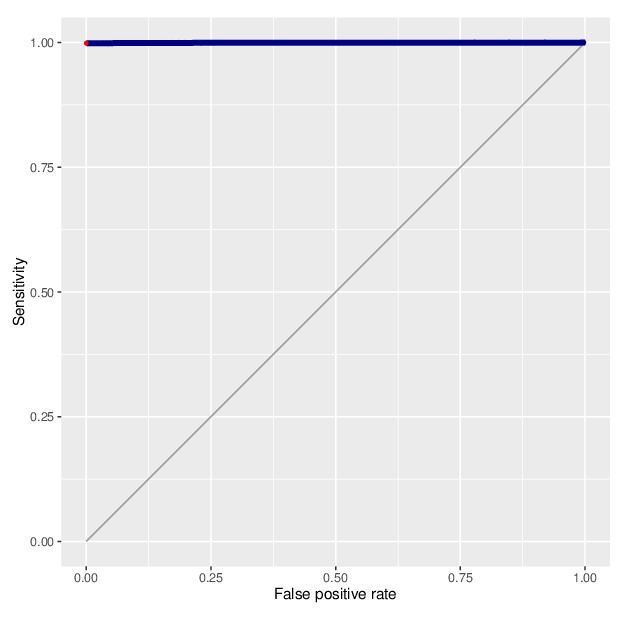
Change of table dimensions / metric related to accuracy as Greedycut progressively removes probes and samples. Accuracy is calculated by treating the retained entries as predictive of reliable measurements. The red circle, if present, marks the last iteration that was executed.
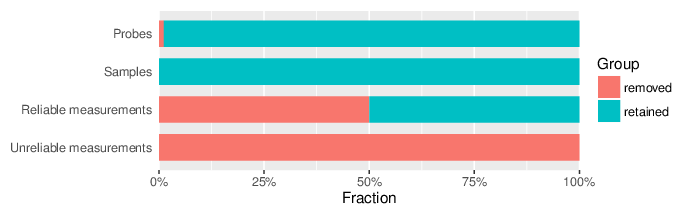
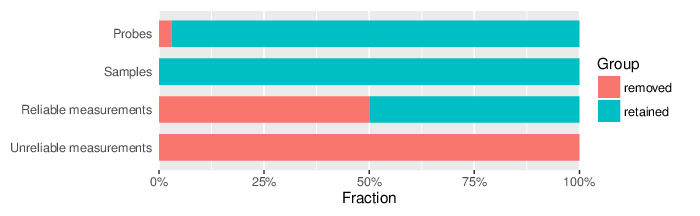
Based on the criteria described above, 781 probes and 0 samples were filtered out. Links to the lists of removed items are given below.
| Type | Removed | Table |
| Probes | 781 | removed_sites_greedycut.csv |
| Samples | 0 |